Bitcoin Transaction Fee

One of the benefits of Bitcoin is the ease of sending it to anyone anywhere across the globe as long as the person has a Bitcoin address. While there is no intermediary like banks or agents, you have to pay a certain fee for every transaction.
What are Bitcoin Transaction Fees?
In general terms, Bitcoin transaction fee is the cost you incur whenever you send Bitcoins from one Bitcoin wallet to another. It is the difference between the amount of Bitcoins spent and the amount received. This fee is usually paid to miners to incentivize them to add your transaction to the blockchain, and therefore, is also referred to as miners’ fee. The sender is solely responsible for paying the transaction fees, and the Bitcoin’s design allows him or her to choose how much fee to pay.
Current Bitcoin Transaction Fee
How much are Bitcoin transaction fees?
Knowing the fees you have to pay to access a service is very important in determining the usefulness of any system. The BTC transaction fee you pay depends on how fast you would like your transaction completed. This is because a Bitcoin block can only accommodate 1 MB of transactions per 10 minutes. Therefore, to get your transaction processed faster, you will need to outbid other users. It’s important to note that the total Bitcoin amount doesn’t matter. For instance, if your transaction is 300 bytes, you’ll pay the same amount whether you’re sending 0.01 Bitcoins or 1 million Bitcoins.
The fee you pay only affects the time you have to wait until the first confirmation and recipients usually require between 2 to 6 confirmations to consider the transaction valid. Once your transaction gets the first confirmation, the waiting time for other confirmations does not depend on the transaction fee paid.
- Next block fee – The fee you need to pay for your transaction to be mined on the next block (10 minutes)
- 3 blocks fee – The fee you need to pay for your transaction to be mined within three blocks (30 minutes)
- 6 blocks fee – The fee you need to pay for your transaction to be mined within six blocks (1 hour)
Average Bitcoin network fee
Transaction fees usually fluctuate every day, depending on network demand. When the number of transactions is high, Bitcoin fee rises, and when there are fewer transactions, the fee reduces. The average Bitcoin transaction fee over the past five years has been $1.63. Therefore, you can expect to pay between $0.03 and $ 3 based on the size of your transaction, network congestion, and other factors.
Bitcoin high transaction fees
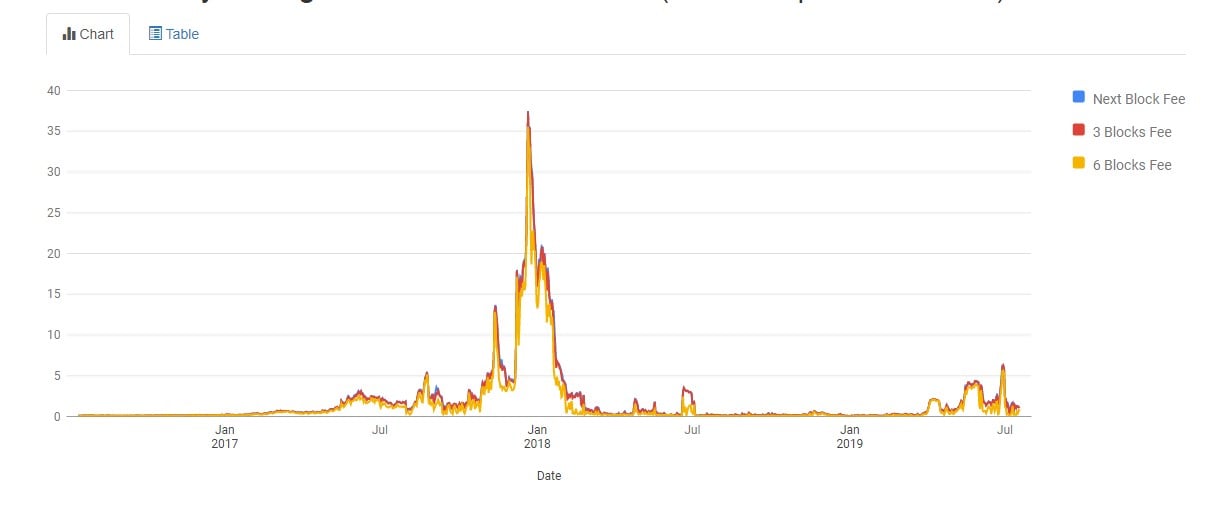
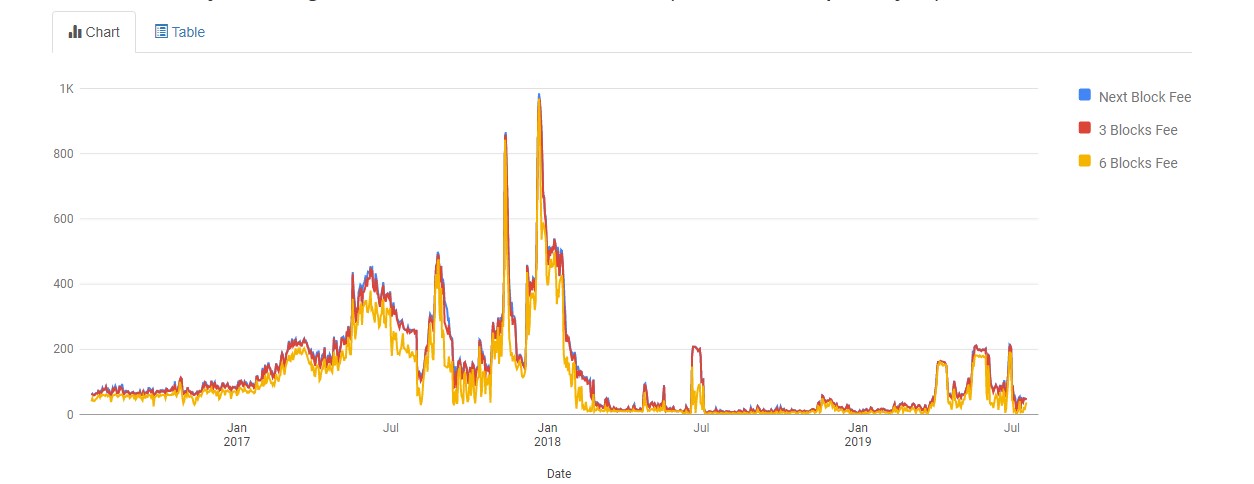
Back in Q4 of 2017, Bitcoin transaction costs were very high, rising up to $30-$60 per transaction. However, no one paid much attention to fees because they were so small compared to the price of one Bitcoin.
Current Bitcoin minimum fee
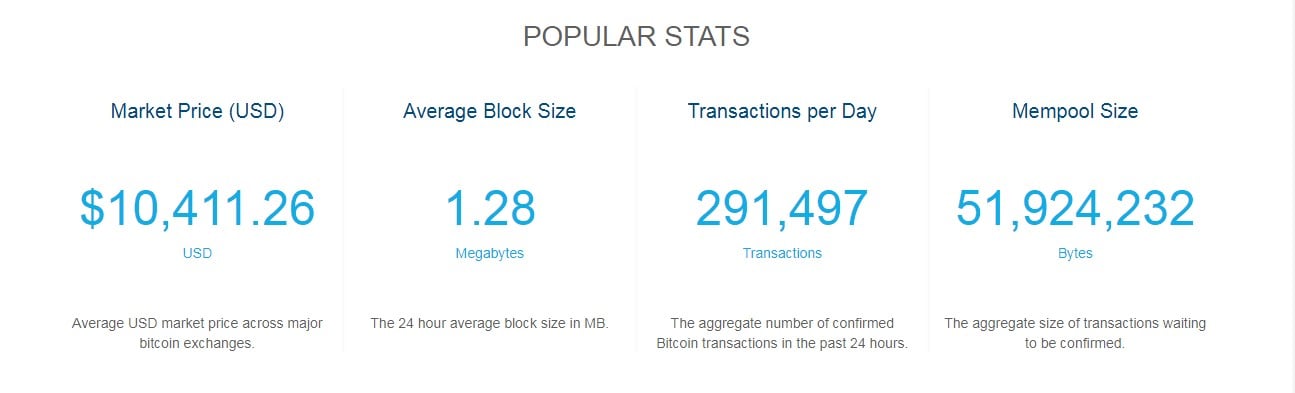
Today, things have changed and Bitcoin transaction fees are not as costly. At present, there are more than 50 million transactions pending in the Mempool, and Bitcoin’s blockchain is validating an average of more than 290,000 transactions every day.
At the time of writing, the suggested minimum fee to get your transaction placed in the next block is 49 satoshis per byte, which is equivalent to $1.27 per transaction. To get a place in the next 1-3 blocks, you will need to attach 47 satoshis per byte ($1.22 per transaction). And the least transaction fee you can pay is 14 satoshis ($0.38 per dollar).
For more info and the current average fees, check http://bitcoinfees.info
BTC vs. Bitcoin Cash average transaction fee
At present, the BCH transaction fee to get your transaction confirmed in the next block is $0.0016, and the median fee is $0.0009. BTC fees are much higher than BCH miner fees because of the limit on block capacity.
You can access BCH average transaction costs on https://blockchair.com/bitcoin-cash/charts/average-transaction-fee-bch?
How to Calculate BTC Transaction Fees
Every Bitcoin user and trader wants to know how to determine the fee they should pay for a transaction to be successful. However, calculating these fees can be quite challenging and confusing for most people.
Bitcoin transfer fee calculation
Here are some insights on how it’s done:
As we’ve already mentioned, the space available for transactions in a block is limited to just 1 MB in the Bitcoin Network. A Bitcoin transaction is 400 bytes on average, meaning a block can only accommodate about 2500 transactions. Therefore, when you transact, your transaction competes in the market for a place in the 1 MB block. Since Bitcoin is decentralized, the fees are determined by the market forces. However, miners maximize their profits by keeping unconfirmed transactions (Bitcoin Mempool) in descending order of transaction fees. Therefore, users who want quicker transactions pay higher fees, thereby pushing the average fees higher.
Bitcoin fee estimation
What is the formula for calculating Bitcoin Blockchain fees?
Experts say that the fee is calculated using a formula that involves multiplying the size of the transaction in bytes with the median byte size. You then take the answer in satoshis and divide it by 100 million. This gives you the transaction cost in Bitcoins, which you can then convert to USD to get your BTC transaction fee. Unfortunately, for most users, this is quite complicated.
Bitcoin fee estimator
Fortunately, there are easier ways to check transaction fees and avoid all these technical details. Many trading platforms and web-based Bitcoin wallets have built-in Bitcoin fee calculators that help users to get the fee estimates. There are also web services like bitcoinfees.info, bitcoinfees.earn.com, and buybitcoinworldwide.com/fee-calculator/ that provide Bitcoin transaction fees.
Bitcoin lower transaction fee
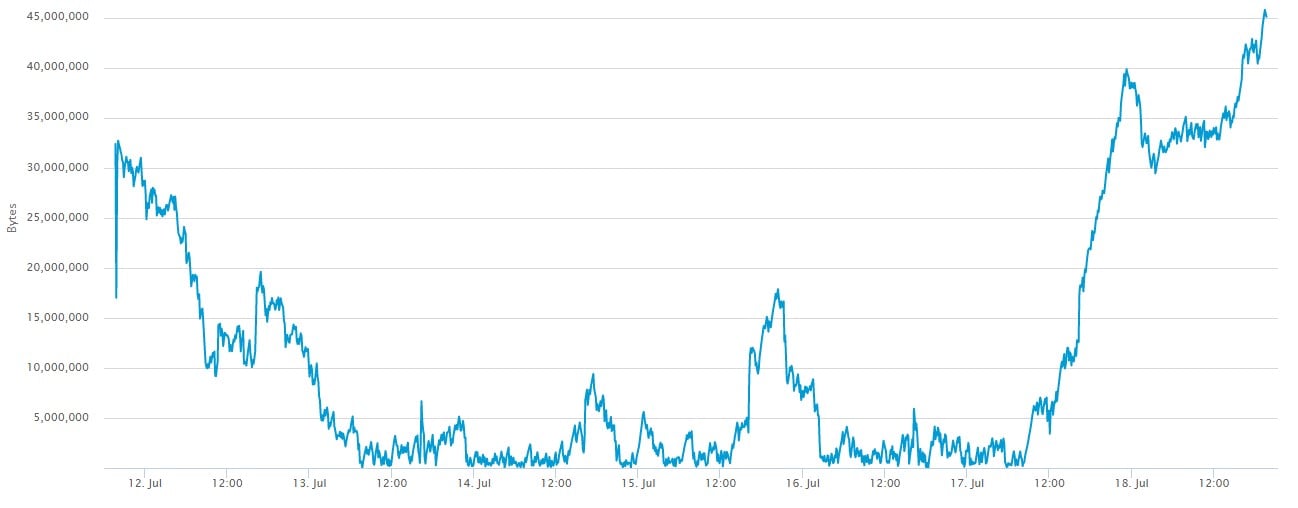
If you want lower transaction costs, it’s recommended that you use SegWit address. SegWit is a software upgrade that minimizes transaction data. SegWit transactions take less time and are usually cheaper because you’re transferring less data over the network. If you are not in a rush, you can also opt to wait for the number of unconfirmed transactions in the Mempool to drop, which will allow you to take advantage of lower average transaction costs.
You can check Mempool size on www.blockchain.com/en/charts/mempool-size or btc.com/stats/unconfirmed-tx.
Blockchain wallet fees
Blockchain wallet uses a dynamic fee structure, whereby it calculates the appropriate fee for your transaction based on the transaction size and the current network conditions. As more and more people learn about Bitcoins and start to use it, the number of transactions continues to rise, and there’s no sign of slowing down soon. This increase creates periods of congestion on the network hence the need for a more reliable fee structure. A dynamic fee structure ensures fast and reliable transaction confirmation times and provides best value, regardless of congestion on the Bitcoin network.
The dynamic fee structure raises or lowers transaction fees depending on the changes in network volume. Therefore, a transaction of $300 bytes may require a lower fee during a period of low activity or a higher fee if sent during a period of network congestion.
Low transaction fee Bitcoin wallet
Blockchain wallet allows you to choose between a “Priority fee” and a “Regular fee”. The Priority fee will get your transaction included in a block within the hour, but at a higher cost. If you want to pay a low transaction fee, choose a “Regular fee”. However, it will take a bit more time hence is ideal for users who are not in a hurry to have the transaction completed.
Blockchain wallet also has a “Customize Fee” feature that allows advanced users to set customized fees for their transactions.
How Much Bitcoin Transaction Fees should you pay for Confirmed Transaction?
Although there is technically no obligation to attach fees to a Bitcoin transaction, miners are also not obliged to add any transaction in the block they’re confirming. Therefore, it makes sense to attach a fee to incentivize the miners to confirm your transaction. So, whenever you want to send Bitcoins, you have to pay the miners.
Since miners will always prioritize transactions with the highest fee per byte, you should pay the highest possible fee if you want your transaction confirmed in the shortest time, usually 5 to 15 minutes. However, if you’re not in a hurry, pay lower fees and your transaction will be confirmed within the next 3 or 6 blocks.
What Do Bitcoin Miner Fees Do?
Bitcoin miners have machines that secure the network and confirm all transactions that pass through it every day by adding blocks to the blockchain. They are responsible for adding transactions to the blockchain and once added; no one can reverse a transaction. Miners are incentivized by block rewards and the transaction fee they get when they confirm transactions, and will naturally try to maximize their profits. To maximize their profits, they can either create more blocks or include more of those transactions that attach higher fees. However, creating more blocks is a cost-intensive process and takes time.
Therefore, Bitcoin miners use the miner fees to decide which transactions to confirm first in order to maximize their profits. If you attach a high fee, your transaction will be confirmed in the next block, and if you attach a low miner or no fee at all, your transaction will take longer to be confirmed. In fact, miners rank transactions in order of the miner fee attached.
How to confirm Bitcoin transactions
When you make a Bitcoin transaction, it flows into the Mempool where it joins other unconfirmed transactions. Every 10 minutes, miners create a new block and add it to the Bitcoin blockchain through the Bitcoin mining process. The block verifies and records the transaction, and the transaction is then said to have been confirmed by the Bitcoin network. A new block is then created every 10 minutes, reconfirming the transaction. Some services require one confirmation while other companies need more than one.
Note that, the more the confirmations a transaction has had, the harder it is to reverse it.
How to check Bitcoin confirmations:
When you make a Bitcoin transaction, your wallet will allow you to view the transaction on a block explorer. Alternatively, it can give you a transaction ID that looks like this: 6a83810802e113b7059254ef0a8a5c3635db3754186451dd982f56253b2d5c4ff7. If you want to check the number of confirmations, copy the ID and paste it into a block explorer like blockchain.com/explorer
What happens if a transaction is not confirmed?
Bitcoin transactions without a miner fee will eventually be confirmed or rejected by the network. If your transaction is rejected, all the funds will be returned to your wallet (typically in between 1 and 7 days).
Why are Miner Fees so High?
Miner fees are determined by the Bitcoin network demand since the network space is limited to 1MB per block. Just like the law of supply and demand applies in products and services, it works in a similar manner in the blockchain. When demand is higher than the supply, prices rise, and when the demand is low, it falls. Demand, in this case, is the number of people transacting in Bitcoins and supply is the network space which is always constant. Therefore, Bitcoin miner fees rise higher when there are more people sending more transactions.
Daily Average Bitcoin Transaction Fee Chart (In Dollars per Transaction)
You can get the daily average Bitcoin miner fee from https://bitcoinfees.info/
Daily Average Bitcoin Fees (In Satoshis per Byte)
Source: https://bitcoinfees.info/
Conclusion
Bitcoin fees have always been a concern for users and traders. And while they rise and fall depending on the Mempool size, a lot has been done to lower the average Bitcoin transaction costs. From the introduction of Segwit technology to transaction batching, innovations around Bitcoin have greatly reduced transaction fees, making transfers more affordable compared to how they were in 2017. Moreover, there’s a lot that you too can do to mitigate the cost of sending your coins. Some of the ways include:
- Transact when there are less unconfirmed transactions on Bitcoin’s blockchain. You can do this by monitoring the Mempool size.
- Use fee recommendation sites such as bitcoinfees.info and bitcoin.earn.com to get an insight into the latest fee structure.
- Use wallets that have implemented SegWit address to reduce your transaction size
- Use wallets that allow you to choose the transaction fee you want to pay
There are several platforms that show you daily Bitcoin fee estimates that you need to attach to get your transaction confirmed. Therefore, don’t get lost trying to calculate the fees yourself unless you’re an expert.
Sources
https://www.buybitcoinworldwide.com/fee-calculator/
https://www.blockchain.com/en/charts
https://www.blockchain.com/en/charts/mempool-size
https://btc.com/stats/unconfirmed-tx
https://www.blockchain.com/explorer
https://support.earn.com/en/articles/64966-how-do-i-calculate-my-transaction-fee
https://news.bitcoin.com/how-to-calculate-bitcoin-transaction-fees-when-youre-in-a-hurry/
https://www.coindesk.com/state-of-blockchains-bitcoin-btc-fees
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Techniques_to_reduce_transaction_fees
https://cryptocurrencyfacts.com/how-do-bitcoin-transaction-fees-work/
https://blockchair.com/bitcoin-cash/charts/average-transaction-fee-bch?
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Miner_fees
https://99bitcoins.com/bitcoin/fees/
https://themoneymongers.com/bitcoin-transaction-fees/
https://support.blockchain.com/hc/en-us/articles/360000939883-Explaining-bitcoin-transaction-fees
https://blog.blockchain.com/2016/03/16/introducing-dynamic-fees/
Author Profile

Fat Finger
My name is Phat Fin Ge, but most people just call me Fat Finger or Mr. Finger.
Many years ago, I was a trader on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. I became so successful that my company moved me to their offices on Wall Street. The bull market was strong, but my trading gains always outperformed market averages, until that fateful day.
On October 28th, 1929, I tried to take some profits after Charles Whitney had propped up the prices of US Steel. I was trying to sell 10,000 shares, but my fat finger pressed an extra key twice. My sell order ended up being for 1,290,000 shares. Before I could tell anyone it was an error, everyone panicked and the whole market starting heading down. The next day was the biggest stock market crash ever. In early 1930, I was banned from trading for 85 years.
I went back to Hong Kong to work at my family's goldfish store. Please come and visit us at Phat Goldfish in Kowloon, only a 3 minute walk from the C2 MTR entrance.
I thought everyone would forget about me and planned to quietly return to trading in 2015. To my horror, any error in quantity or price which cause a problem kept getting blamed on Fat Finger, even when it was a mix up and not an extra key being pressed. For example, an error by a seller on the Tokyo Stock Exchange was to sell 610,000 shares at ¥6 instead of 6 shares at ¥610,000. That had nothing to do with me or with how fat the trader's finger was, but everyone kept yelling, "Fat Finger! Fat Finger!" In 2016, people blamed a fat finger for a 6% drop in the GBP. It really was a combination of many things, none to do with me or anyone else who had a wider than average finger.
Now that I can trade again, I'm finding forex more interesting than stocks. I've been doing some research on trading forex and other instruments and I'll be sharing it here.
If you see any typing errors, you can blame those on my fat finmgert. If you see any strange changes in price, it's not my fault.
Info
637 Views 0 CommentsComments
Table of Contents
Recent
-
Bitcoin Fundamental Briefing, March 2024 Demystifying Cryptocurrency Nodes: Deep Dive into Polygon Node Ecosystem Strategies for Trading Forex on a Budget Bitcoin Fundamental Briefing, February 2024 Bitcoin Fundamental Briefing, January 2024 Strategic Asset Allocation Techniques for Currency Traders Bitcoin Fundamental Briefing, December 2023 Bitcoin Fundamental Briefing, November 2023